How Huddle Boards and Gantt Charts Work Together To Delivery Revenue
Most managers are not dictated a specific way of organizing their team. Instead, they are given broad, measurable goals and told to deliver results within a specified budget and timeframe. So it stands to reason that over time, as managers in different functions begin working together to deliver value to the customer (aka a “valuestream”), a plethora of team collaboration and resource management tools begin to multiply across the enterprise. Depending on the size, geographic dispersion and mix of trades in any one department, there may even be up to four different work management methodologies deployed.
The general purpose of project management tools is to help make a company more efficient and boost the bottom line. Luckily, there are systems and frameworks for helping interconnect lean management, Agile/Scrum and Gantt/Waterfall.
Agile in Context
Agile is a work management philosophy generally used in the IT and software development industry but has permeated almost every non-technical industry. It was originally devised as an alternative to linear, long-running Software Development project methodologies and offers a more iterative, time-boxed, modular approach to work break-down.
So if a set of work tasks are thought to be achievable in a fixed window of time, we need a way to organize the tasks and assign them to various team members. Usually the time period (aka “Sprint”) is measured in weeks, not months, so the rate of day-to-day progress is very high and therefore daily meetings are needed to maintain order and increase collaboration/communication.
To implement such a methodology, the concept of a Scrum Board was created — taking from the concept of a rugby scrum which has both sides jostling for the ball on the ground. Eventually one side or the other obtains control and begins the passing game.
A huddle board is simply one type of Scrum Board — a visual tool used to implement agile philosophies into various business environments.
SunPower improved project collaboration and increased productivity resulting in shorter and more stable project life cycles. Download case study.
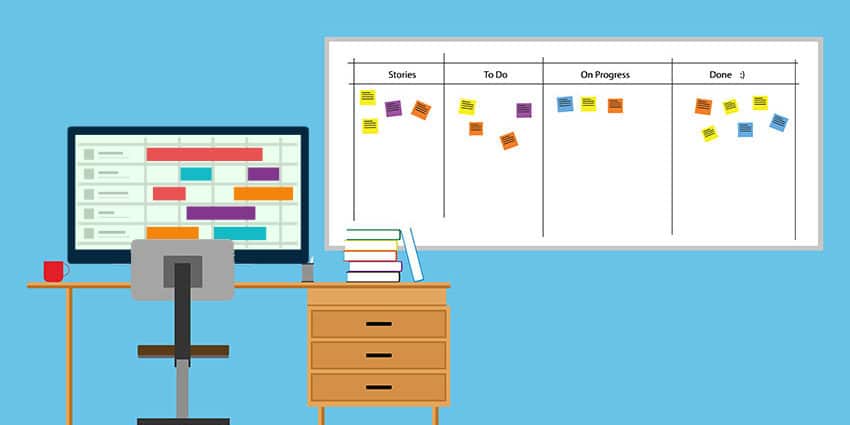
What is a Huddle Board?
A huddle board is a standardized visual tool meant to help teams collaborate on and visualize all the tasks necessary to complete a project or manage daily/weekly work in a repetitive business process.
A huddle board is often organized to contain all the ongoing tasks for a particular “sprint” (one of the iterations of agile projects). They often take the form of a plain white dry erase boards, and they’re most often covered in a variety of sticky notes with tasks penned on each one.
Huddle boards help organizations visualize their priorities for a particular stage in a project and help focus in on potential areas of improvement. For example, some healthcare organizations actually call daily meetings around the department’s huddle board, which outlines all the daily priorities for that particular team. This ensures everyone is on the same page and that everyone and expectations and tasks is set out in very clear terms.
Huddle boards also allow team members to track the state of a task as it moves from backlog to completion. It’s easy to visually see the various stages of change that a particular task goes through as it passes from column to column on the Huddle board.
What is a Gantt Chart?
For work plans with definitive delivery dates, fairly well-known work processes to deliver results and low R&D requirements (no “unknowns”) with few external risk factors which can materially change the project scope, it makes sense to plan the work from start to finish in linear fashion. In these cases a more waterfall-like work management methodology is used to break work down into manageable phases, then packages, and finally sub-tasks to acurately orchestrate/synchronize dependencies between tasks. Hence the term Work Breakdown Structure (aka “WBS”) to mean the sum total of work packages represented as distinct, hierarchical modules.
The Gantt chart was invented by Henry Gantt circa 1910 to visualize exactly this type of work break-down. It outlines each task or work package as a bar on a graph with dates across the top header row axis (x-axis) and tasks down the left side (y-axis). These tasks may take several hours or even several days/weeks to complete. Tasks can be organized into bunches or groupings of like-tasks.
Bringing it all Together
Because a company implements and delivers its product to many, many customers repeatedly, it becomes very adept at understanding what it takes to deliver a particular product or service. We therefore tend to see this customer-facing work predominantly managed by Gantt charts.
Invariably, however, internal engineering or service support teams need to assist in the early design or configuration of a solution for the customer. These teams may utilize the Huddle Board and therefore need a simple mechanism to link visual cards on a Huddle board to a specific WBS task on the Gantt. This has two concurrent benefits: 1. Each team can work independent of the other utilizing the visual tool which best supports the resource management and work synchronization methodology within their teams and; 2. Each team can be immediately alerted to a mis-match between delivery timeframes — i.e. the Gantt task may require an end-date of Thursday 5pm but the Huddle board card is in a 2 week Sprint which ends on Friday. The 1 day gap is immediately highlighted on both the Huddle board card and Gantt task.
Did you find this work management tip helpful? Leankor’s workflow management system can help your team become even more efficient.